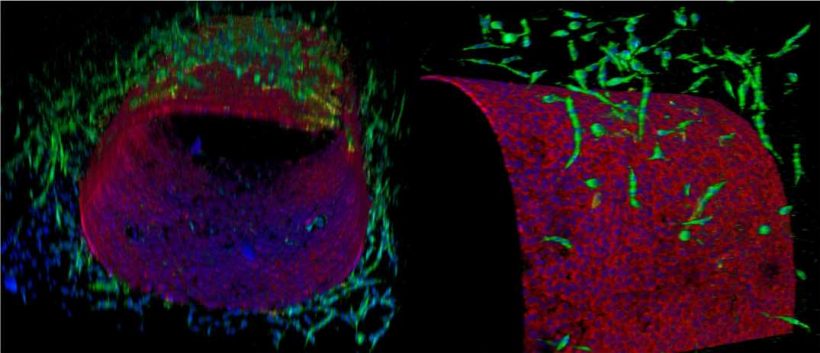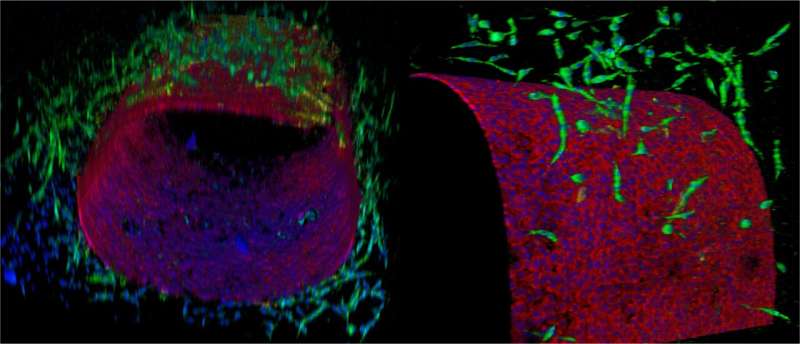
Currently, there is little research focused on understanding mechanisms and drug discovery of lymphatic vascular diseases. However, conditions such as lymphedema, a buildup of fluid in the body when the lymph system is damaged, impact more than 200,000 people every year in the United States alone.
Dr. Abhishek Jain, assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M University, has taken his expertise in organ-on-chip models and applied them to a field they’ve never been used in before, creating the first lymphangion-chip.
To engineer this new device, Jain’s team first developed a new technique to create microfluidic cylindrical blood or lymphatic vessels consisting of endothelial cells, which line blood vessels. It could then use this technique to create a co-cultured multicellular lymphangion, the functional unit of a lymph vessel, and successfully recreate a typical section of a lymphatic transport vessel in vitro, or outside the body.
“We can now better understand how mechanical forces regulate lymphatic physiology and pathophysiology,” Jain said. “We can also understand what are the mechanisms that result in lymphedema, and then we can find new targets for drug discovery with this platform.”
The project is in collaboration with Dr. David Zawieja from the Texas A&M College of Medicine. Their research was published in the Jan. 7 issue of the journal Lab on a Chip.
“Collaborations with Dr. Zawieja and others in the department played a crucial role,” Jain said. “They introduced me to this topic and provided their longstanding expertise that has made it possible for us to create this new organ-on-chip platform and now advance it in these exciting directions using contemporary experimental models.”
Jain said the impact of this work is far-reaching because there is new hope for patients with lymphatic diseases. They can now learn about the biology of these diseases and reach a point where they can be treated.
Source: Read Full Article