New research has led to a new understanding an important driver of recurrent chest infections in children.
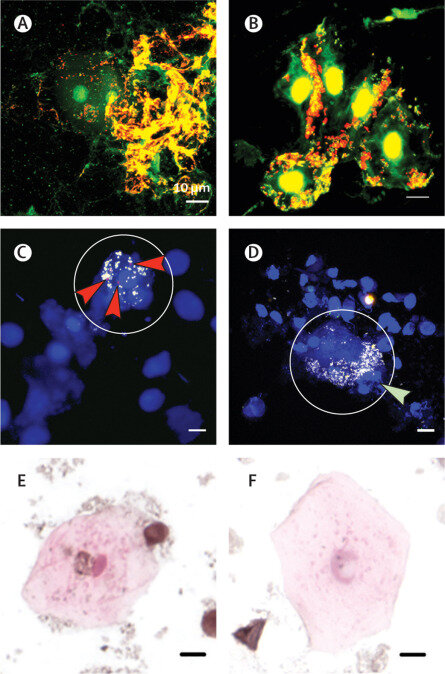
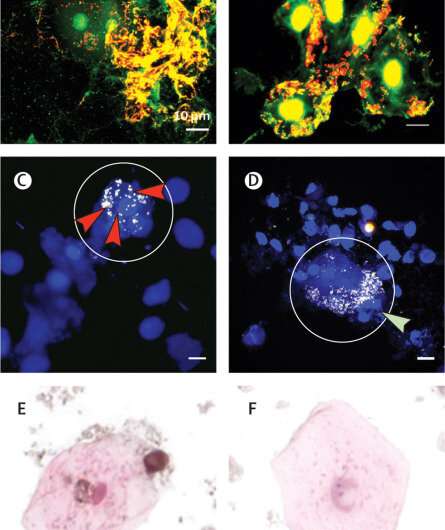
Many children experience a prolonged wet cough after having an acute cough and can develop a condition called protracted bacterial bronchitis or PBB. In a collaborative study published in The Lancet Microbe, researchers from Menzies School of Health Research (Menzies), The Telethon Kids Institute and the University of Western Australia (UWA) used a powerful microscope to discover that some of the kids with persistent wet coughs had a bacterial slime—called a biofilm—in their lungs.
Lead author Dr. Robyn Marsh, Menzies senior research fellow, says children with recurrent PBB are at increased risk of progressing to a severe lung disease called bronchiectasis.
“We know that for most kids with PBB, their cough will get better after they have had a two-week course of antibiotics, but we also know that some kids will have repeated episodes of bronchitis that never seem to get better,” Dr. Marsh said.
“This puts them at risk of developing a severe lung disease called bronchiectasis. We know that chest infections can lead to PBB and bronchiectasis, but the reasons why only some kids respond to antibiotics isn’t always clear.”
The research team used a process known as bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) to collect a sample from the lungs for testing. During the procedure, a sterile solution is used to flush the child’s airways and capture a fluid sample containing the germs that cause the child’s chest infection. This is the first known study to demonstrate a prevalence of biofilm in affected children.
Study co-author Dr. Ruth Thornton a research fellow, UWA Centre for Child Health Research (affiliated with the Telethon Kids Institute) says using the powerful microscope with contrasting colors assisted in locating and identifying the bacterial slime which is present in the affected lungs.
“This is an important discovery as we know that when bacteria live in these slimes they can be more than a thousand times more resistant to antibiotics than the bacteria that cause the acute infections that you take your child to the doctor for. This means that when you stop antibiotics your child is likely to get yet another infection,” Dr. Thornton said.
Professor Anne Chang AM, Menzies Head of Child Health described the study results as an exciting way forward to help treat the children who have been suffering.
Source: Read Full Article